Fatty Liver
Reason for fatty liver, liver inflammation and liver disease
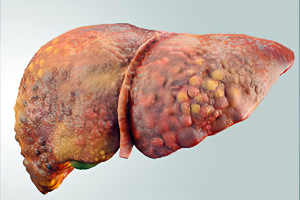
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), on the other hand, is not related to alcohol consumption and is more common. It is closely associated with obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels. NAFLD can also progress to a more severe form called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can cause liver damage and scarring, leading to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Symptoms of fatty liver disease may not appear until the disease has progressed to a more advanced stage. Some common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
Fatty liver, Liver inflammation, Liver disease treatment in Bangalore
Lifestyle Changes: For fatty liver disease, lifestyle modifications are often the first line of treatment. This includes:
Weight Loss: Losing excess weight through a combination of diet and exercise reduces the buildup of fat in the liver. Healthy Diet: An eating pattern with low or almost no saturated fat, sugars, and processed food with a moderate intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide protection and help improve the health status of the liver. Regular Exercise: Physical exercise leads to weight loss and also enhances insulin working levels, resulting in the lowering of liver fat. Limiting Alcohol: Alcohol causes liver injury, so limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption is essential. Medication Review: Some medications can contribute to liver damage. Reviewing medications with a healthcare provider and adjusting or discontinuing them, if necessary, may be beneficial. Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage specific liver conditions: For inflammation, physicians might use anti-inflammatory medicines to control inflammation of the liver or even corticosteroids could be prescribed for the same purpose. Treatment of Underlying Conditions: Addressing associated predisposing elements, like diabetes or hypertension, along with viral hepatitis, will also contribute to the improvement of liver health. Regular Monitoring: Regular testing of liver function through blood tests and conducting imaging studies can be helpful both in terms of tracking the progression of liver diseases and assessing the effectiveness of the treatment. Advanced Therapies: There is a severe condition in which one starts to take advanced therapies, which can complicate such diseases.
Liver Transplant: Patients with late-stage liver disease or liver failure have few options, including a liver transplant as the only potential eventual treatment. Minimally Invasive Procedures: Procedures such as liver biopsy, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), or radiofrequency ablation may be used to diagnose or treat liver conditions so consultation from the Best Liver transplantation doctor in Bangalore.
Nutritional Supplements: Some nutritional supplements, including vitamin E or omega-3 fatty acids, can have positive outcomes for liver health; however, such benefits may have side effects, and these supplements should be used after consultation from the Best Liver surgeon (doctor) in Bangalore.